- How to Adjust X and Y Axis Scale in Arduino Serial Plotter (No Extra Software Needed)Posted 7 months ago
- Elettronici Entusiasti: Inspiring Makers at Maker Faire Rome 2024Posted 7 months ago
- makeITcircular 2024 content launched – Part of Maker Faire Rome 2024Posted 9 months ago
- Application For Maker Faire Rome 2024: Deadline June 20thPosted 11 months ago
- Building a 3D Digital Clock with ArduinoPosted 1 year ago
- Creating a controller for Minecraft with realistic body movements using ArduinoPosted 1 year ago
- Snowflake with ArduinoPosted 1 year ago
- Holographic Christmas TreePosted 1 year ago
- Segstick: Build Your Own Self-Balancing Vehicle in Just 2 Days with ArduinoPosted 1 year ago
- ZSWatch: An Open-Source Smartwatch Project Based on the Zephyr Operating SystemPosted 1 year ago
Virtual Reality App from 219 Design Simplifies the Programming of Robots

While robots may make complicated tasks look easy, programming a robot is anything but – particularly when you’re talking about large, complex industrial robots whirring away in factories. But with a new app developed by product engineering firm 219 Design, anyone should be able to program a robot easily, quickly and in virtual reality.
The concept for the tool arose after 219 Design acquired an HTC Vive virtual reality system and used it to design their first VR app: Interact VR, a tool that allows companies to evaluate products in virtual reality. The success of the app led to more brainstorming about other ways the company could incorporate virtual reality into their product design. They ended up with a new project: an app that uses a VR interface to control a tool in the real world.
The robot’s design was incorporated into an app that serves as a controller. The user, fitted with an HTC Vive, clicks and drags the virtual representation of the robot arm’s end effector in any desired path, while the physical robot follows. To “teach” the robot a new behavior, the user simply clicks a record button before dragging the end effector in the chosen range of movement. Once the recording is finished, the user hits “play” and the robot will repeat the movement
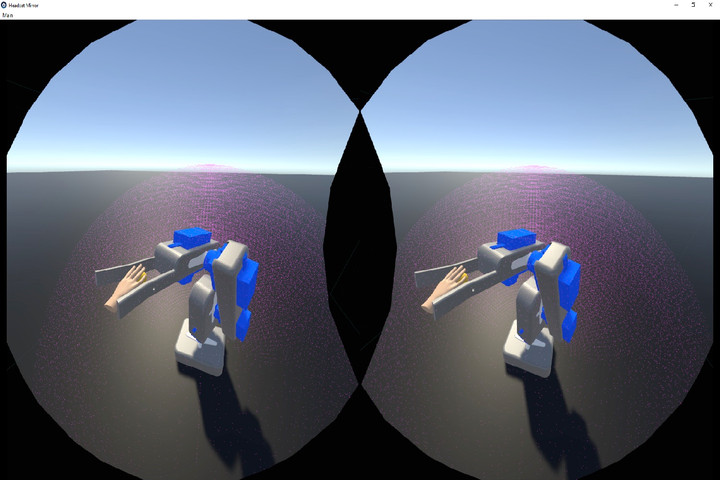
This solution simplifies and brings to real haptic the interfacing with robots, opening interesting scenarios where the natural movement precision is fundamental. Let’s think about telemedicine, surgical robots, bomb removal, hazmat handling and so on!
Source: 3DPrint.com