- How to Adjust X and Y Axis Scale in Arduino Serial Plotter (No Extra Software Needed)Posted 2 months ago
- Elettronici Entusiasti: Inspiring Makers at Maker Faire Rome 2024Posted 2 months ago
- makeITcircular 2024 content launched – Part of Maker Faire Rome 2024Posted 5 months ago
- Application For Maker Faire Rome 2024: Deadline June 20thPosted 6 months ago
- Building a 3D Digital Clock with ArduinoPosted 11 months ago
- Creating a controller for Minecraft with realistic body movements using ArduinoPosted 12 months ago
- Snowflake with ArduinoPosted 12 months ago
- Holographic Christmas TreePosted 12 months ago
- Segstick: Build Your Own Self-Balancing Vehicle in Just 2 Days with ArduinoPosted 1 year ago
- ZSWatch: An Open-Source Smartwatch Project Based on the Zephyr Operating SystemPosted 1 year ago
Coding Pang’s sprite spawning mechanic | Wireframe #10
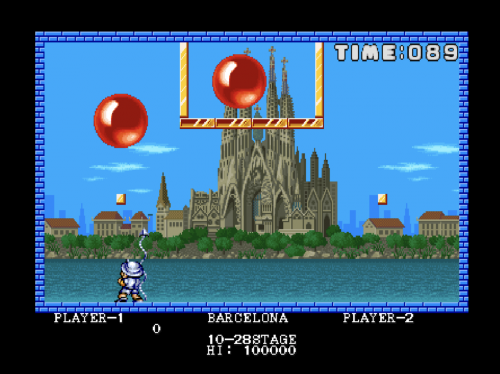
Pang: bringing balloon-hating to the masses since 1989.
Capcom’s Pang
Programmed by Mitchell and distributed by Capcom, Pang was first released as an arcade game in 1989, but was later ported to a whole host of home computers, including the ZX Spectrum, Amiga, and Commodore 64. The aim in Pang is to destroy balloons as they bounce around the screen, either alone or working together with another player, in increasingly elaborate levels. Destroying a balloon can sometimes also spawn a power-up, freezing all balloons for a short time or giving the player a better weapon with which to destroy balloons.
Initially, the player is faced with the task of destroying a small number of large balloons. However, destroying a large balloon spawns two smaller balloons, which in turn spawns two smaller balloons, and so on. Each level is only complete once all balloons have been broken up and completely destroyed. To add challenge to the game, different-sized balloons have different attributes – smaller balloons move faster and don’t bounce as high, making them more difficult to destroy.
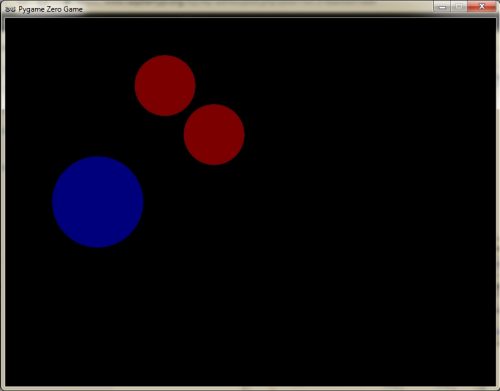
Rik’s spawning balloons, up and running in Pygame Zero. Hit space to divide them into smaller balloons.
Spawning balloons
There are a few different ways to achieve this game mechanic, but the approach I’ll take in my example is to use various features of object orientation (as usual, my example code has been written in Python, using the Pygame Zero library). It’s also worth mentioning that for brevity, the example code only deals with simple spawning and destroying of objects, and doesn’t handle balloon movement or collision detection.
The base Enemy class is simply a subclass of Pygame Zero’s Actor class, including a static enemies list to keep track of all enemies that exist within a level. The Enemy subclass also includes a destroy() method, which removes an enemy from the enemies list and deletes the object.
There are then three further subclasses of the Enemy class, called LargeEnemy, MediumEnemy, and SmallEnemy. Each of these subclasses are instantiated with a specific image, and also include a destroy() method. This method simply calls the same destroy() method of its parent Enemy class, but additionally creates two more objects nearby — with large enemies spawning two medium enemies, and medium enemies spawning two small enemies.

Here’s Rik’s example code, which recreates Pang’s spawning balloons in Python. To get it running on your system, you’ll first need to install Pygame Zero – you can find full instructions here. And you can download the code here.
In the example code, initially two LargeEnemy objects are created, with the first object in the enemies list having its destroy() method called each time the Space key is pressed. If you run this code, you’ll see that the first large enemy is destroyed and two medium-sized enemies are created. This chain reaction of destroying and creating enemies continues until all SmallEnemy objects are destroyed (small enemies don’t create any other enemies when destroyed).
As I mentioned earlier, this isn’t the only way of achieving this behaviour, and there are advantages and disadvantages to this approach. Using subclasses for each size of enemy allows for a lot of customisation, but could get unwieldy if much more than three enemy sizes are required. One alternative is to simply have a single Enemy class, with a size attribute. The enemy’s image, the entities it creates when destroyed, and even the movement speed and bounce height could all depend on the value of the enemy size.
You can read the rest of the feature in Wireframe issue 10, available now in Tesco, WHSmith, and all good independent UK newsagents.
Or you can buy Wireframe directly from us – worldwide delivery is available. And if you’d like to own a handy digital version of the magazine, you can also download a free PDF.

Make sure to follow Wireframe on Twitter and Facebook for updates and exclusives, and for subscriptions, visit the Wireframe website to save 49% compared to newsstand pricing!
The post Coding Pang’s sprite spawning mechanic | Wireframe #10 appeared first on Raspberry Pi.















